How Oculomotor Eye Muscles move your eyes
For Myopia Treatment Stretch Oblique Eye Muscles
The Oculomotor Muscles: An Overview
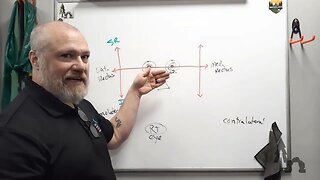
There are six main muscles involved in moving each eye. Four of these are the rectus muscles—superior, inferior, medial, and lateral—that move the eye up, down, inwards, and outwards, respectively. The other two are the oblique muscles—superior and inferior—which allow the eye to roll and look diagonally.
Superior Rectus: This muscle moves the eye upwards and contributes to inward rolling of the eye.
Inferior Rectus: It moves the eye downwards and also assists in the outward rolling of the eye.
Medial Rectus: The primary function is to pull the eye inwards, towards the nose.
Lateral Rectus: This muscle moves the eye away from the nose.
Superior Oblique: It allows the eye to roll inward and look down.
Inferior Oblique: This muscle lets the eye roll outward and look up.
These muscles are innervated by three cranial nerves—the oculomotor nerve (III), the trochlear nerve (IV), and the abducens nerve (VI). The oculomotor nerve controls most of the eye movements by innervating the superior, inferior, and medial rectus muscles, and the inferior oblique muscle. The trochlear nerve innervates the superior oblique muscle, and the abducens nerve controls the lateral rectus muscle.
How Oculomotor Muscles Move Your Eyes
The movement of the eye is a coordinated effort that requires precise control over the oculomotor muscles. When you look in a particular direction, the brain sends signals through the cranial nerves to the relevant muscles, instructing them to contract or relax. For instance, looking to the right involves contracting the right lateral rectus and the left medial rectus simultaneously, while the muscles on the opposite sides relax.
The coordination between these muscles is crucial for maintaining binocular vision, allowing the eyes to focus on a single point and perceive depth. Any imbalance or dysfunction in these muscles can lead to issues such as double vision (diplopia), strabismus (misalignment of the eyes), and other visual disturbances.
Eye Conditions Related to Oculomotor Muscles
Several conditions can affect the function of the oculomotor muscles, leading to visual impairment:
Strabismus: A misalignment of the eyes due to uneven muscle strength or control.
Diplopia: Double vision caused by muscles not working together correctly.
Nystagmus: Involuntary eye movement resulting from abnormal function in the areas of the brain that control eye movements.
Oculomotor nerve palsy: Paralysis or weakness in the muscles innervated by the oculomotor nerve, affecting eye movement and pupil size.
Conclusion
The oculomotor eye muscles play a vital role in our ability to see the world around us. Their precise control and coordination allow us to focus, track moving objects, and perceive depth. Understanding how these muscles work offers insights into the complexity of the visual system and the importance of maintaining eye health. Regular eye examinations can help detect any issues with these muscles early, ensuring timely treatment and management to preserve vision.
-
 6:42
6:42
Sviaton
1 month agoHow to heal your eyesight with light eye muscle stretching
54 -
 2:19
2:19
Sviaton
1 month agoHow to heal strabismus with eye exercises naturally
38 -
 1:53
1:53
Natural Cures
1 year ago $0.03 earnedDo This Movement With Your Eyes Every Day to Improve Your Eyesight
229 -
 13:50
13:50
UncivilizedVitality
2 years agoOrbital Anatomy: Extraocular Muscles
8 -
 1:36
1:36
Macropod
9 years agoClose up of eye in motion
5.8K -
 6:28
6:28
Vital Wellbeing
1 year ago#91 Lessons on Health - MOVE - eye fitness
-
 1:19
1:19
DrJulieVisionforLife
2 years agoKoosh Ball Activity for Amblyopia and Eye Hand Coordination
9 -
 1:53
1:53
Natural Cures
2 years ago $0.01 earnedImprove Your Vision With These Easy Exercises
134 -
 3:15
3:15
Dr. Eric Berg
7 years agoHow to Improve Eyesight With Best Exercise – Dr. Berg
15 -
 0:11
0:11
mahora76
11 months agoOpsoclonus Myoclonus Syndrome- A Child with “Jumping Vision”
10