Hydrogen Bonding|Types of Hydrogen Bonding| Application|2023|AIM Pharma
Hydrogen bonding is a special type of dipole-dipole attraction between molecules, not a covalent bond to a hydrogen atom. It results from the attractive force between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a very electronegative atom such as a N, O, or F atom and another very electronegative atom. atom in another molecule.
= O
= N
= H
Hydrogen bonding between two water (H2O) molecules. Note that the O atom in one molecule is attracted to a H atom in the second molecule. Hydrogen bonding between a water molecule and an ammonia (NH3) molecule. Note that the N atom in the NH3 molecule is attracted to a H atom in the H2O molecule.
Physical Consequences of Hydrogen Bonding
At 25oC, nitrosyl fluoride (ONF) is a gas whereas water is a liquid. Why?
ONF and water have about the same shape.
ONF has a higher molecular weight (49 amu) than water (18 amu).
Conclusion: London dispersion forces not responsible for the difference between these two compounds.
ONF and water have the same dipole moment.
Conclusion: dipole-dipole forces not responsible for the difference between these two compounds.
ONF cannot form hydrogen bonds; water can form hydrogen bonds.Hydrogen bond is a electrostatic attraction between a hydrogen atom which is bond to a more electronegative atom such as Nitrogen, Oxygen, fluorine. These are two types of hydrogen bonds :- 1) Intermolecular Hydrogen bonding :- It occurs between two separate molecules. Eq :- H−F...... H−F......
-
 59:52
59:52
Studytutorialpull.com
6 months agoChemistry bonding part1
33 -
 6:03
6:03
MercolaMarket
11 months agoHow H2 MOLECULAR HYDROGEN Can Help You Improve Your Health
991 -
 7:28
7:28
MercolaMarket
1 year ago $0.05 earnedDr. Mercola Demonstrates How to Use H2 Molecular Hydrogen
314 -
 10:31
10:31
AV
7 months ago#333 Hydrogen-specific Solutions
4 -
 1:11
1:11
etfDiscovery
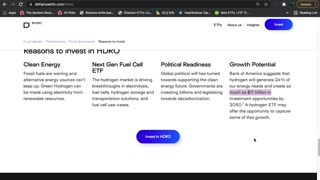
2 years agoHDRO ETF Introduction (Hydrogen)
12 -
 13:20
13:20
Organic Chemistry I & II
2 years ago $0.10 earnedBonding Overview
100 -
 8:00
8:00
AchieveYourPotential
1 year agoIonic Bonding part 1
-
 2:57
2:57
health, science and energy show
4 months ago $0.05 earnedrobust health with hydrogen
57 -
 0:58
0:58
Synergy Science
2 years agoHow Do You Keep the Hydrogen in Your Water Without It Dissolving Quickly Into the Air?
73 -
 15:13
15:13
Hydrogen Power Gas
1 year agothings to consider hydrogen hot rodding
13